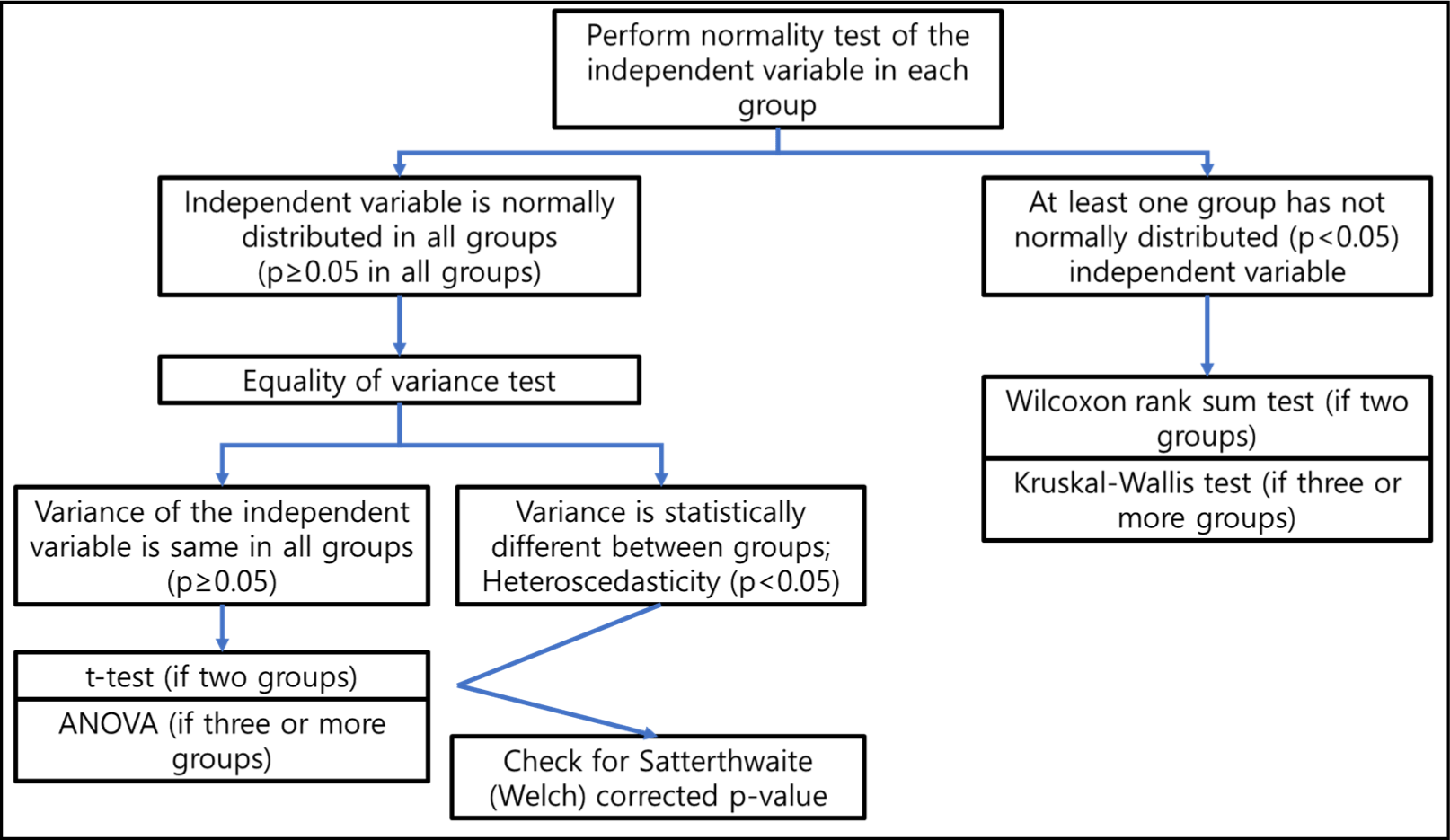
Methods for testing statistical differences between groups in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
Seung Won Lee
Life Cycle 2022;2:e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e1
ABSTRACT
In medical research, when independent variables are categorical (i.e., dividing groups), statistical analysis is often required. This situation mostly occurs on randomized controlled trials and observational studies that have multiple patient groups. Also, when analyzing continuous independent variables in a single patient group, breakpoints can be...
|
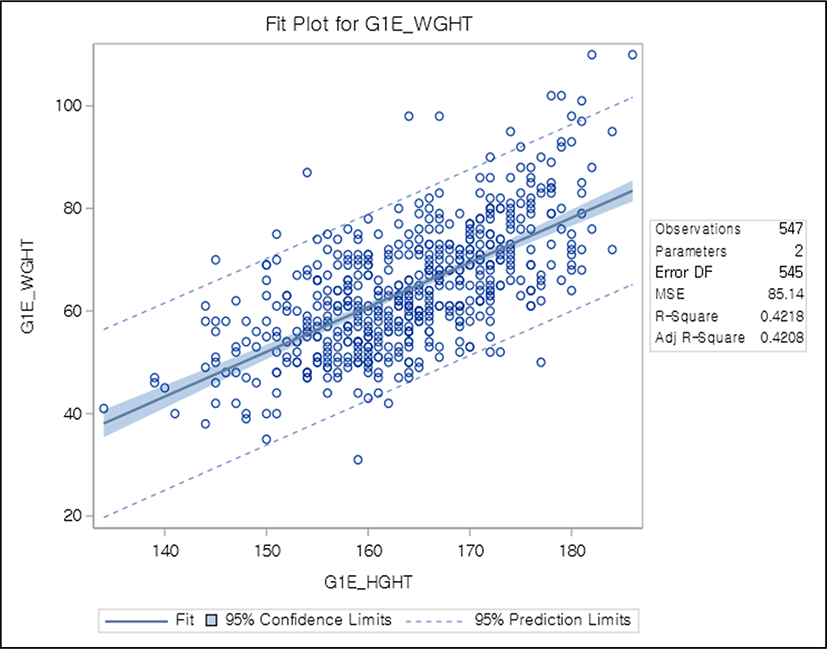
Regression analysis for continuous independent variables in medical research: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
Seung Won Lee
Life Cycle 2022;2:e3
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e3
ABSTRACT
Variables measured in medicine are usually continuous, such as blood pressure, serum glucose, and drug dosage. There are statistical methods to confirm whether these variables act as independent variables that cause an outcome. Most of these methods are types of regression analysis. In this article, starting with a simple correlation coefficient, l...
|
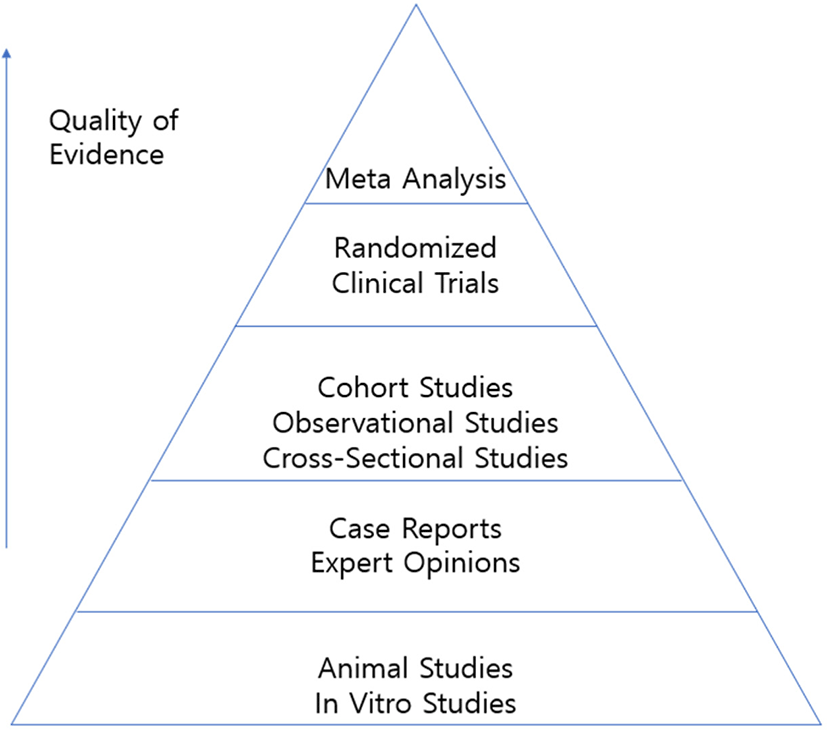
PRISMA 2020 statement and guidelines for systematic review and meta-analysis articles, and their underlying mathematics: Life Cycle Committee Recommendations
Seung Won Lee, Min Ji Koo
Life Cycle 2022;2:e9
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e9
ABSTRACT
The paper discussed the overall aspects of systematic review and meta-analysis and explored the main mathematical context of meta-analysis. This included various methods of analyzing the effect size and obtaining the average effect size depending on the variable type. In doing so, methods of obtaining effect sizes in continuous outcome variables, c...
|
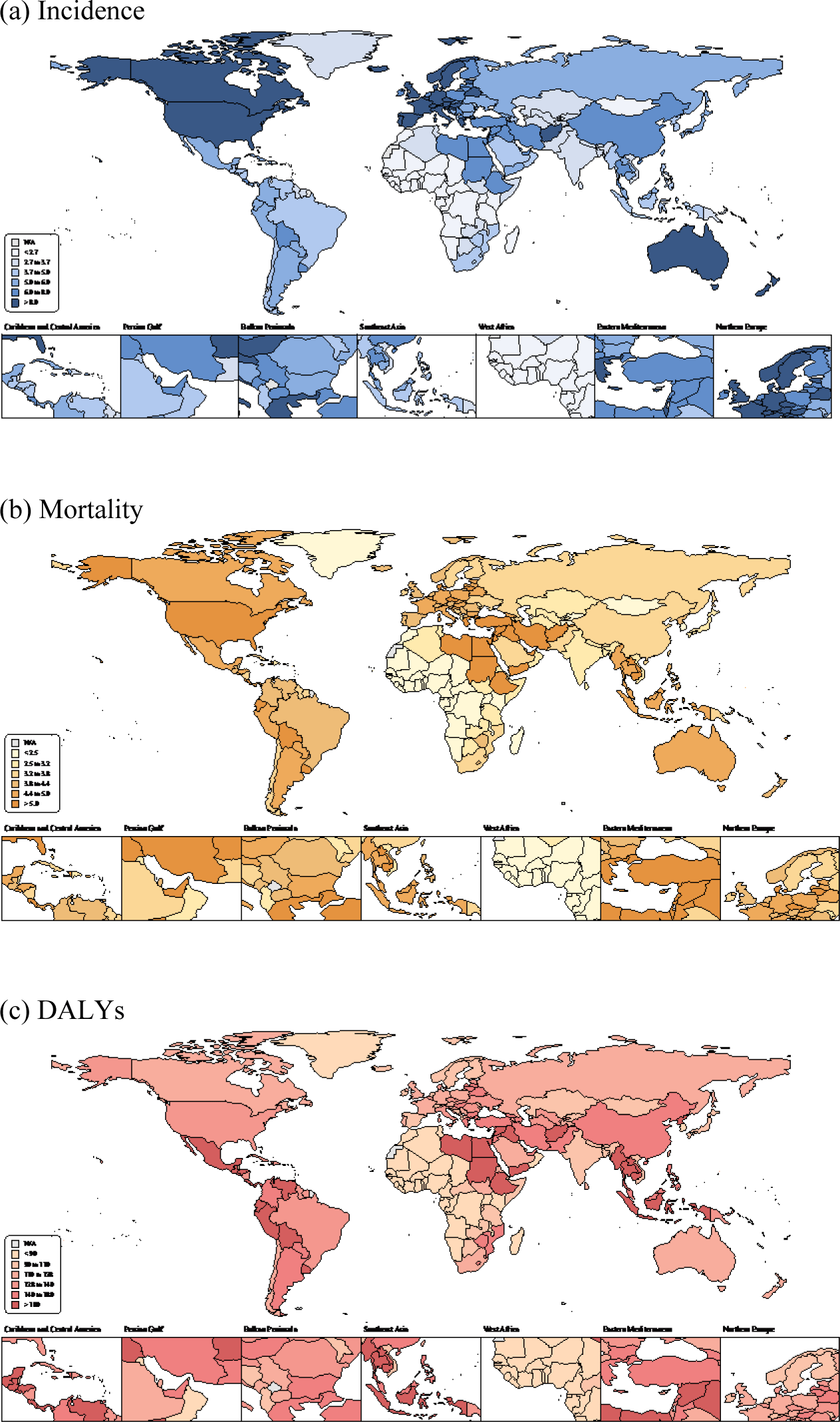
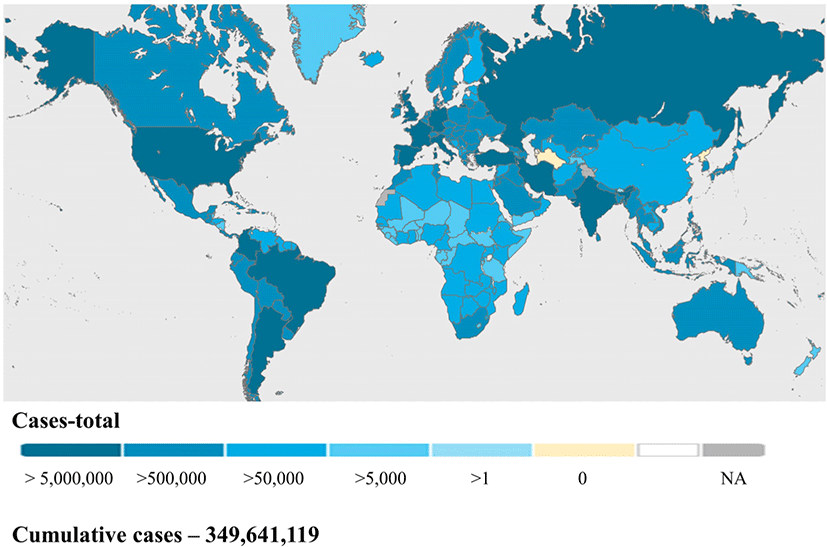
Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality of COVID-19 in 237 countries and territories, January 2022: a systematic analysis for World Health Organization COVID-19 Dashboard
So Young Kim, Abdullah Özgür Yeniova
Life Cycle 2022;2:e10
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e10
ABSTRACT
Objective: To estimate global, regional, and national incidences and mortality of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in 237 countries and territories since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic to 31 January, 2022. Methods: Comprehensive estimates were produced through global, regional, and national studies of cumulative severe acute respirato...
|
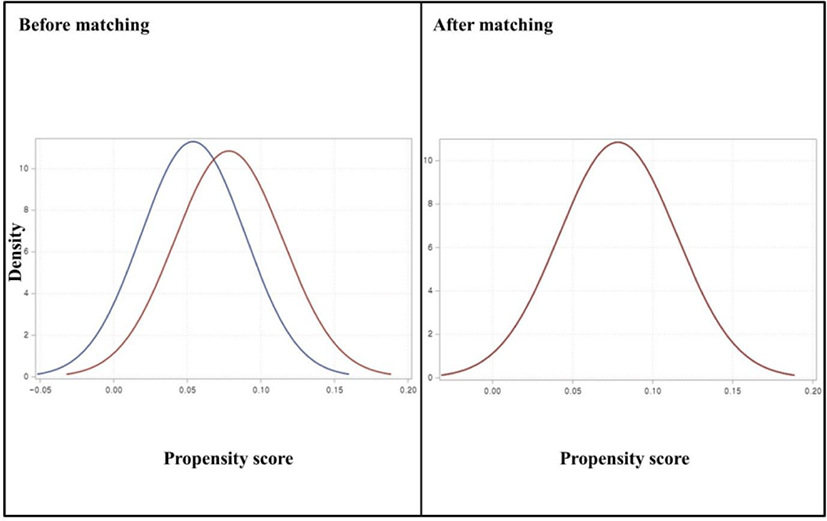
Propensity score matching for causal inference and reducing the confounding effects: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
Seung Won Lee, Krishna Prasad Acharya
Life Cycle 2022;2:e18
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e18
ABSTRACT
Since the development of research methodology, there has always been keen interest in developing the accuracy of the research by comparing covariates. Propensity score is useful when the research covers many variables which are not intended to be included as independent variables, thus allowing the removal of certain covariates from the model. This...
|
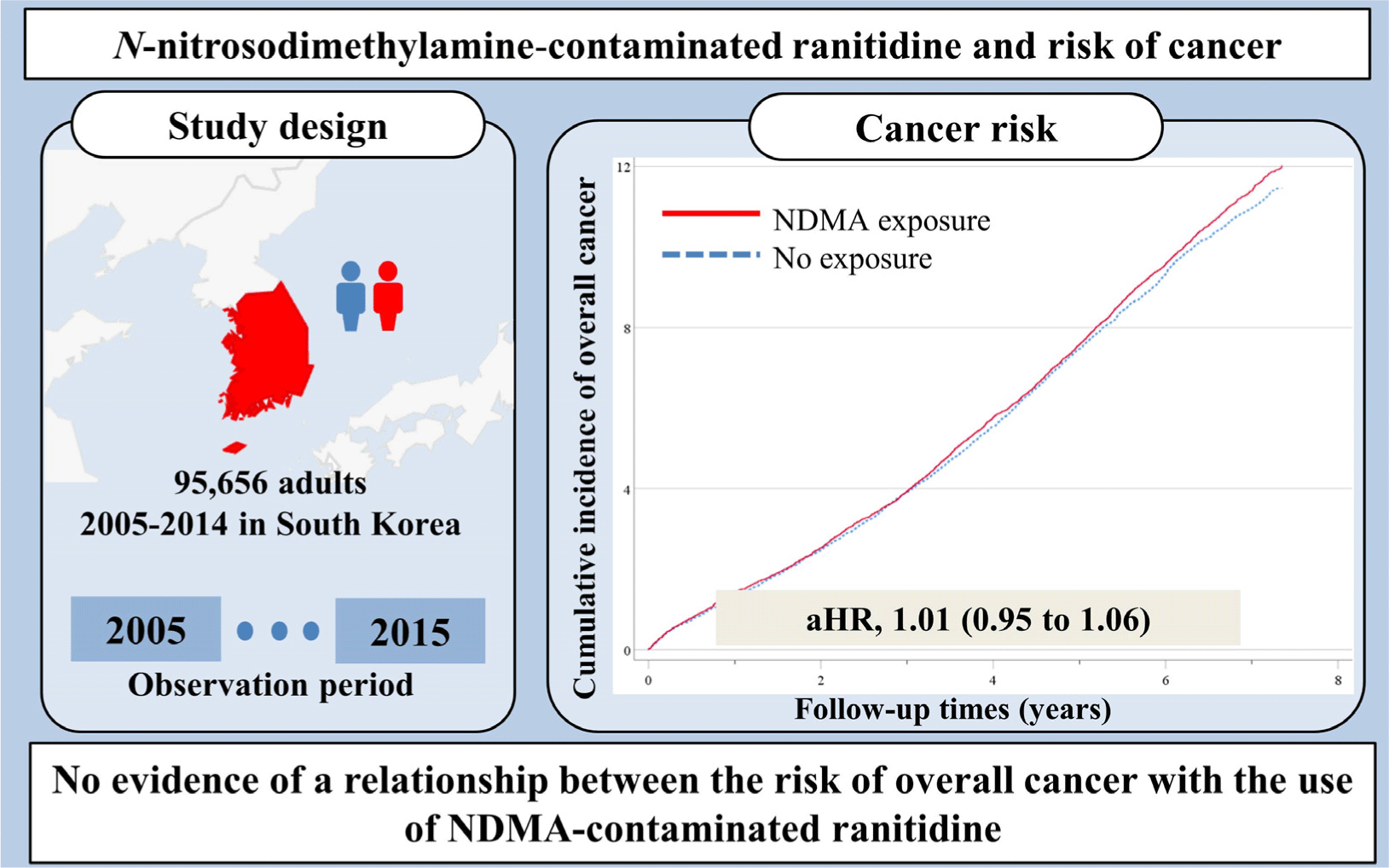
N-Nitrosodimethylamine-contaminated ranitidine and risk of cancer in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study
In Kyung Yoo, Dominic C. Marshall, Joo Young Cho, Hae Won Yoo, Seung Won Lee
Life Cycle 2021;1:e1
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2021.e1
ABSTRACT
Objective: On September 2019, the United States Food and Drug Administration announced that some ranitidine products were contaminated with unacceptable levels of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA). We aimed to determine whether the use of ranitidine that was potentially contaminated with NDMA, rather than another histamine H2-receptor antagonist (H2 bl...
|
Global Burden of Disease study at the World Health Organization: research methods for the most comprehensive global study of disease and underlying health policies
Lee Smith, Jae Il Shin, Soo Young Hwang, Kalthoum Tizaoui, Elena Dragioti, Louis Jacob, Karel Kostev, Seung Won Lee, Ai Koyanagi
Life Cycle 2022;2:e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e8
ABSTRACT
The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) is a compass that navigates researchers and clinicians in discovering the latest knowledge and the current status of health for populations and countries worldwide. The GBD helps to present various methods in evaluating health-related quality of life and assess the health burden, economic burden, years of life los...
|
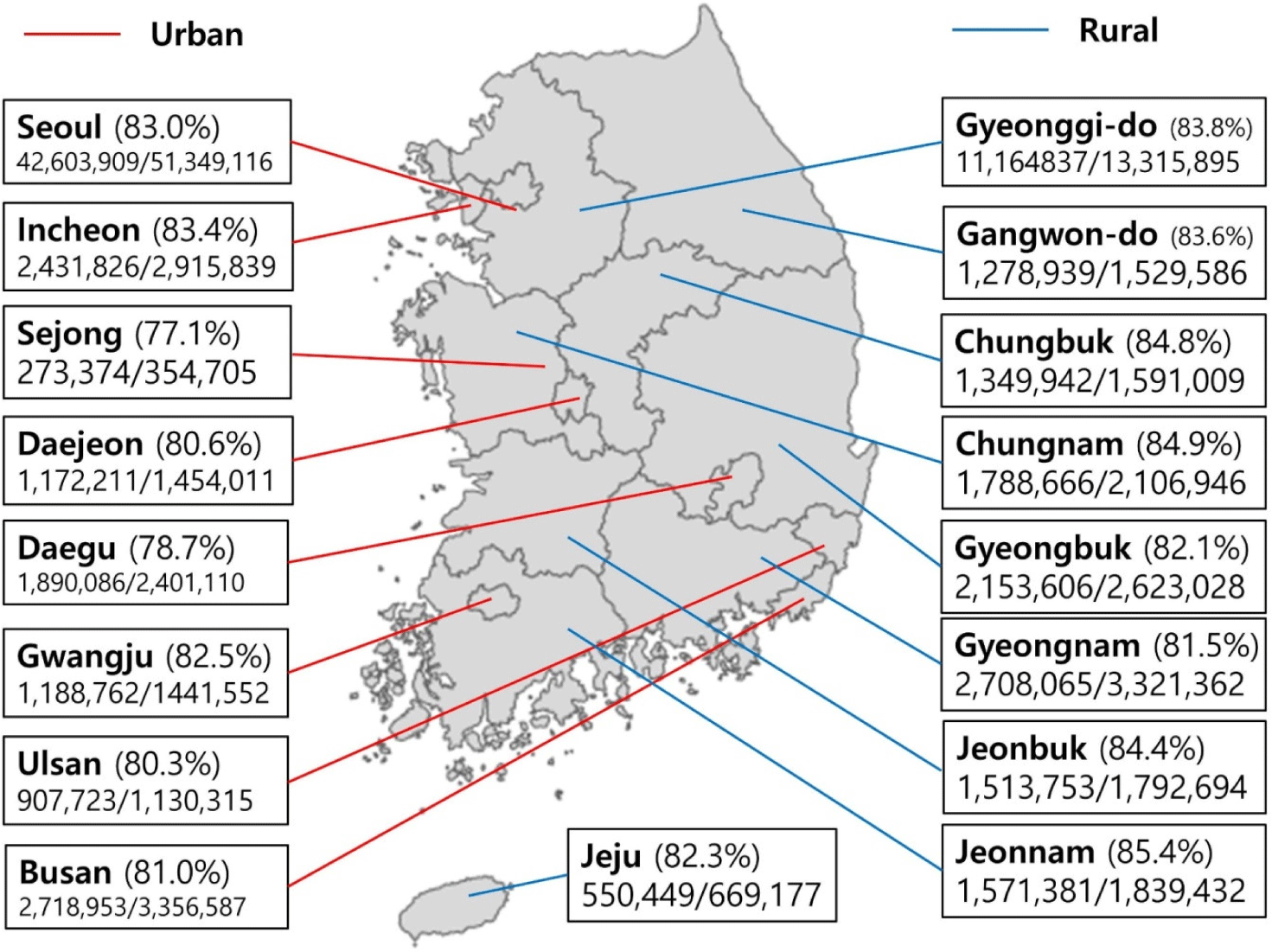
Nationwide COVID-19 vaccination coverage and COVID-19 incidence in South Korea, January 2022: a national official report
So Young Kim
Life Cycle 2022;2:e2
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2022.e2
ABSTRACT
Objective: To reduce the risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) illness, and COVID-19 related death, all persons in South Korea should stay up to data with recommended COVID-19 vaccinations. This study investigated the rates and effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccina...
|
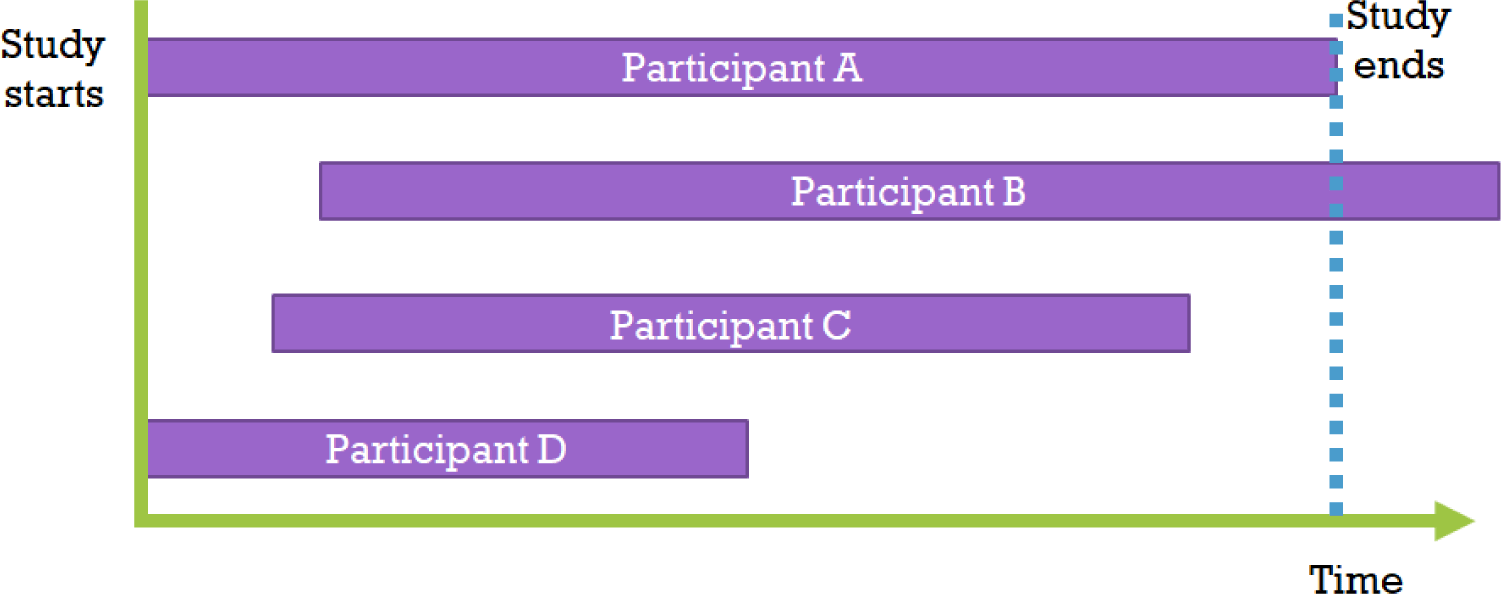
Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards regression in survival analysis: statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee
Seung Won Lee
Life Cycle 2023;3:e8
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2023.e8
ABSTRACT
In medical research, analyzing the time it takes for a phenomenon to occur is sometimes crucial. However, various factors can contribute to the length of survival or observation periods, and removing specific data can lead to bias results. In this paper, we discuss the Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression model, which are t...
|
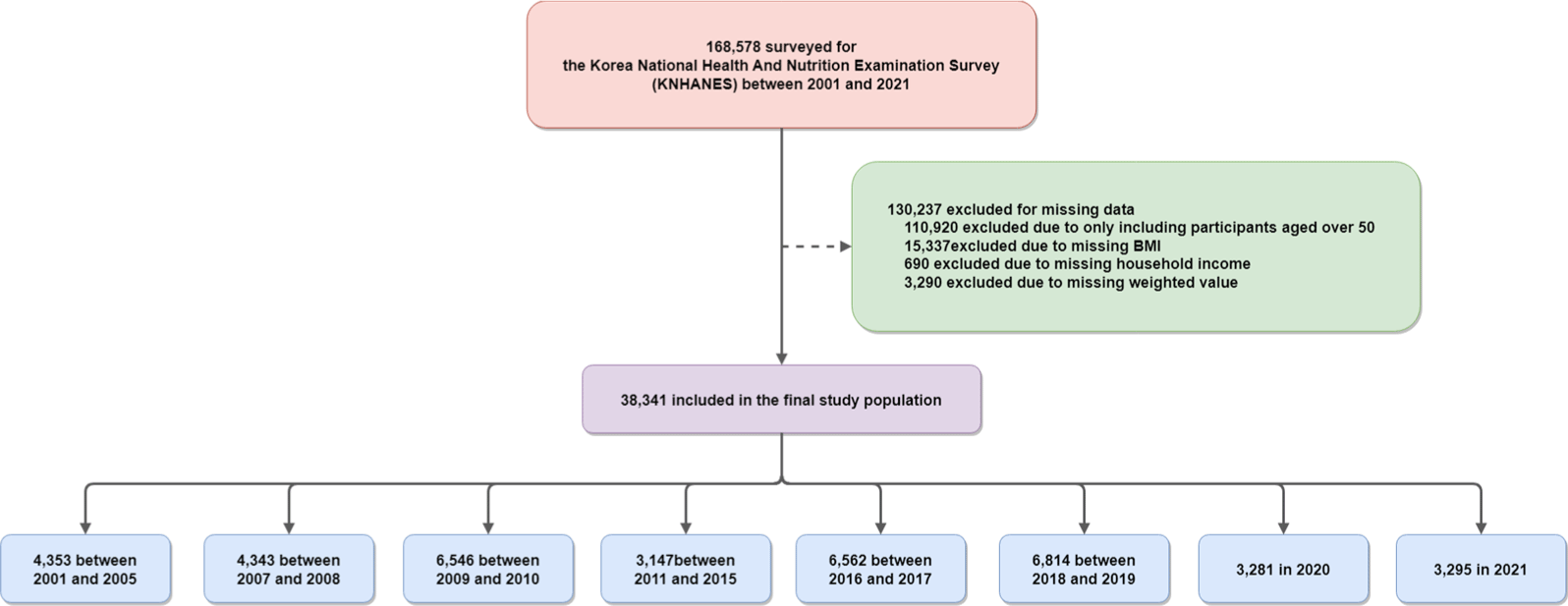
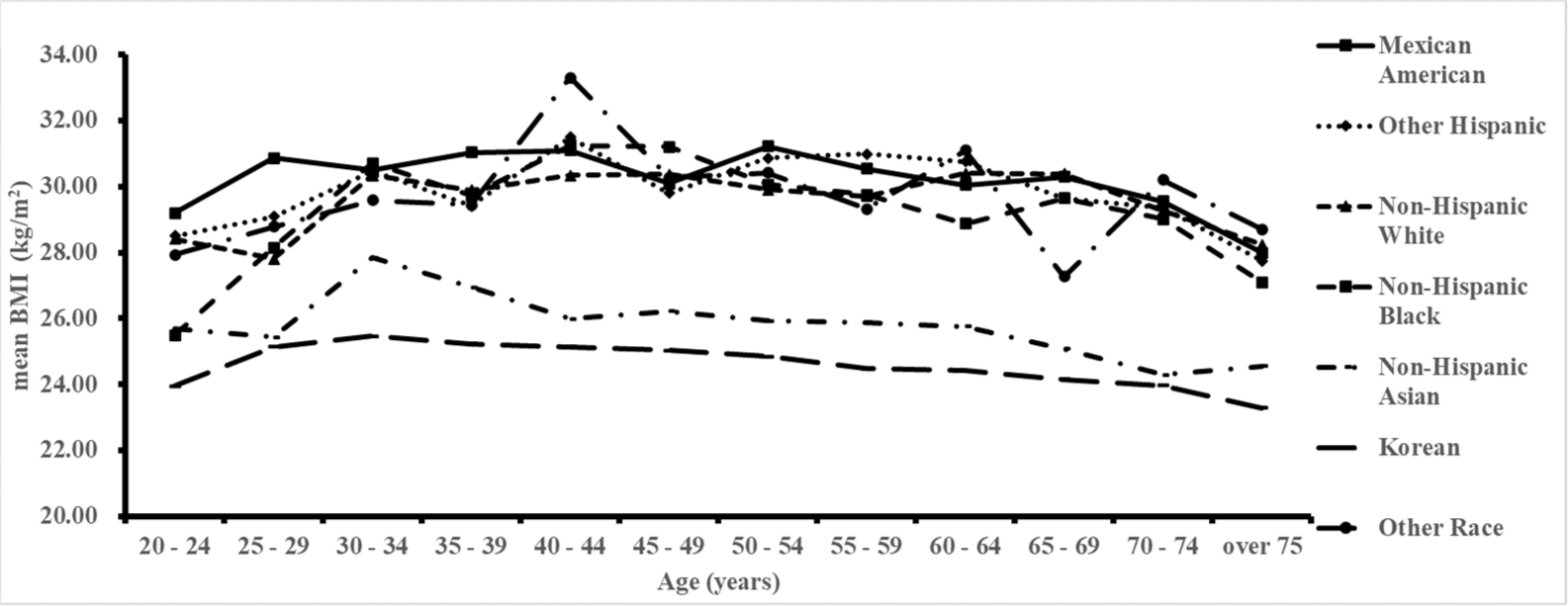
Age, ethnic, and sex disparity in body mass index and waist circumference: a bi-national large-scale study in South Korea and the United States
Seounghyun Eum, Sang Youl Rhee
Life Cycle 2023;3:e4
https://doi.org/10.54724/lc.2023.e4
ABSTRACT
The study investigated age, ethnic, and sex disparities in body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) in South Korea and the United States. We conducted a bi-national large-scale study and analyzed data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) and the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in the U...
|